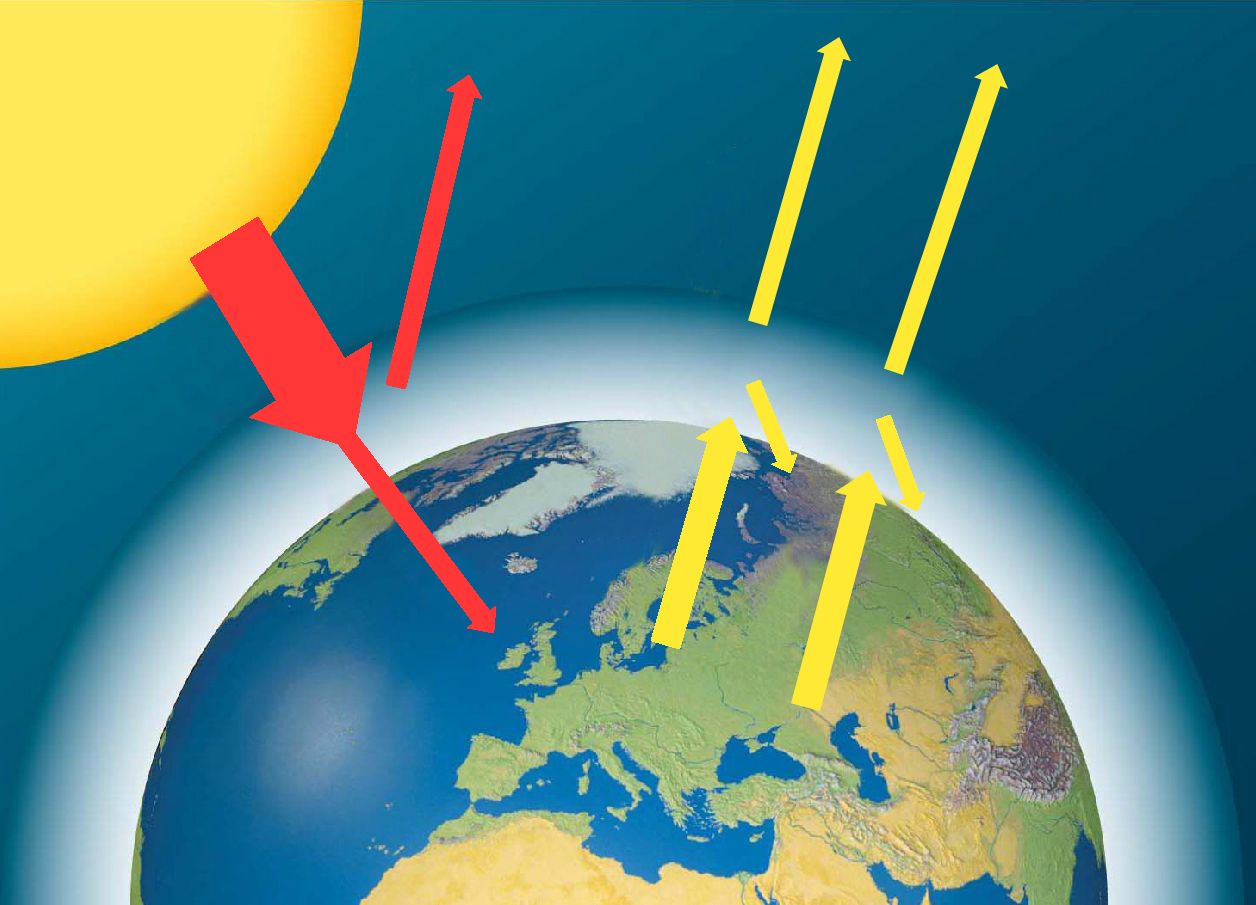
Solar energy enters the atmosphere.
As this short-wave energy passes through the atmosphere it might hit dust particles or water droplets and be scattered or reflected.
Only a little short-wave radiation is absorbed in the atmosphere.
Solar energy heats the Earth's surface, which then radiates long-wave (heat) energy into the atmosphere.
Long-wave energy is quite absorbed by naturally occuring greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Of these, carbon dioxide is by far the most abundant.
Some long-wave energy escapes into space.





