Content
- Newton’s three laws of motion
- Momentum, impact and impulse
- Stability – base of support and centre of mass
Knowledge of the factors that cause movement is based on forces and is underpinned by Newton's laws of motion.
Newton’s laws of motion form the foundation of our understanding of movement and how it occurs. Knowledge of these helps us to understand the demands of performance on the body and explains how successful performance can be developed through the training principles, creating optimum technique.
A body continues in its state of rest or motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force.Joints (structural classifications):
For example, a winger will continue to run in a straight line to score a try unless the opposition comes across to tackle him.
The rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the force causing it and the change takes place in the direction in which the force acts.
For example, if a rugby player, during the execution of penalty, applies a force to a ball, it will move in the direction that this force is applied, and acceleration of the ball will be in proportion to the force applied.
To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
For example, when driving with the ball, a force is applied to the ground by the tackler, at the same time an equal force and opposite force comes back from the ground.
Understanding momentum allows us to understand how mass and velocity influence movement of athletes. Impulse allows us to explain how force and time can cause the athlete to start moving or change direction.
In any system of bodies that exert forces on each other, the total momentum in any direction remains constant unless some external force acts on the system in that direction. Changing mass or velocity can alter momentum.
Impulse is the product of force and the time over which the force is applied, e.g. the follow-through of the boot after the penalty kick allows the player to have the longest contact with the ball and therefore to apply force to the ball for a longer time. This maximises the time that the force is applied.
In many sports, athletes need to be balanced and stable in order to perform successfully. Understanding of the factors that affect balance and stability allow for understanding of performance. Balance and stability can be understood through knowledge of a person’s centre of mass.
An object with a larger base of support is more stable:
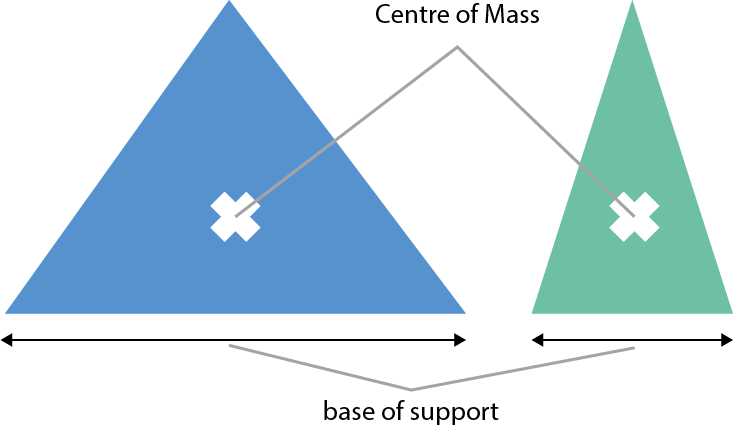
An object with a lower centre of mass is more stable:
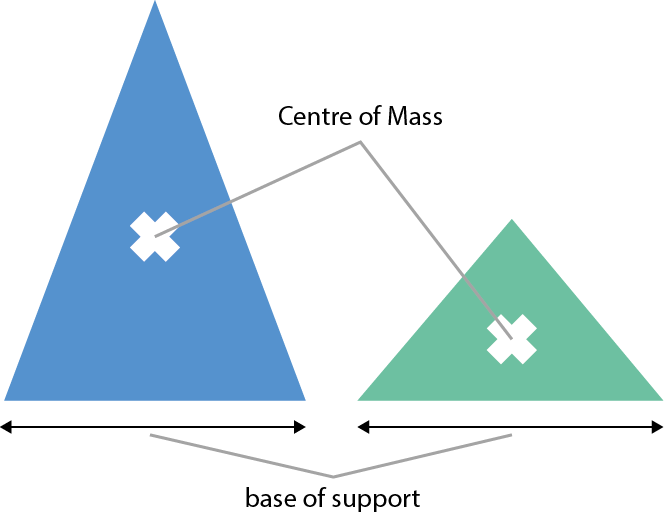
These concepts are vital when getting into the correct body position when in the contact area in rugby, e.g. low wide body position in contact situation.